페르소나 모델 기법을 활용한 위험 상황 조기 감지 및 대화형 경보 생성을 위한 개발 방법
개요
작업자 위험 상황의 조기 감지 및 대화형 경보 생성을 위한 시스템을 구현하기 위해 페르소나 모델 기법을 사용할 수 있습니다. 이 기술에는 위험 감지 및 대응을 개인화하기 위한 자세한 작업자 프로필을 만드는 작업이 포함됩니다. 이 시스템은 오디오, 비디오, 레이더와 같은 센서의 실시간 데이터를 활용하고 사전 정의된 작업자 페르소나를 기반으로 위험 상황을 동적으로 예측하고 대응합니다.
주요 개념
페르소나 모델:
페르소나는 일반적인 행동, 움직임, 작업, 환경적 상호 작용을 포함하는 작업자의 상세한 프로필입니다.
페르소나는 역할(예: 기계 운영자, 유지보수 작업자), 신체적 능력, 위험 노출 수준에 따라 분류됩니다.
대화형 경보:
맞춤형 알림: 페르소나를 기반으로 긴급성, 전달 모드(오디오, 진동, 시각적) 및 콘텐츠 측면에서 알림이 맞춤설정됩니다.
피드백 메커니즘: 작업자는 경보 시스템과 상호 작용하여 문제를 확인하거나 해결할 수 있으므로 동적 위험 완화가 보장됩니다.
개발 방법
1. 페르소나 모델 정의
데이터 수집:
다음을 사용하여 근로자의 일반적인 행동, 움직임 및 작업에 대한 데이터를 수집합니다.
움직임 패턴에 대한 비디오 모니터링.
음성 명령이나 조난 호출에 대한 오디오 분석.
반복적인 작업을 식별하기 위한 작업 로그입니다.
페르소나 예시:
페르소나 A: 기계 조작원
임무 : 중장비를 운전합니다.
위험: 움직이는 부품에 대한 근접성, 피로로 인한 오류.
페르소나 B: 유지보수 작업자
임무: 장비 수리, 제한된 공간에서의 작업.
위험: 낙상, 위험 물질 노출.
세분화:
작업자를 저위험, 중간 위험, 고위험과 같은 범주로 나누거나 업무 및 환경에 따라 분류합니다.
2. 위험 감지 모델
센서 융합:
다음의 데이터 결합:
비디오(위험 구역 또는 물체에 대한 근접성 감지).
레이더(움직임을 추적하고 위험 구역에서 넘어지거나 고정된 위치를 감지합니다).
오디오(조난 신호 또는 경고음을 인식).
행동 분석:
개인별 패턴을 사용하여 위험 상황을 예측합니다.
예: 페르소나 A(기계 조작자)의 경우 레이더가 움직이는 컨베이어 벨트 근처에서 오랫동안 움직이지 않는 상태를 감지하면 시스템은 이를 잠재적인 위험으로 표시합니다.
3. 조기 발견 프레임워크
머신러닝 모델:
동영상: 객체 감지 및 자세 추정(예: 객체의 경우 YOLO, 인간 자세의 경우 OpenPose).
오디오: Whisper 또는 SpeechBrain과 같은 모델을 사용하여 조난 소리를 감지합니다.
레이더: 비행 시간 신호 분석 및 이상 탐지를 사용한 움직임 추적입니다.
이벤트 예측:
LSTM 또는 Transformer와 같은 시퀀스 기반 모델을 사용하여 위험으로 이어지는 패턴을 감지합니다.
예: 작업자 움직임의 갑작스런 정지 + "도와주세요!" 오디오 감지 = 잠재적인 추락.
4. 대화형 경보 시스템
동적 경보 생성:
경보는 개인과 상황의 심각도에 따라 맞춤화됩니다.
페르소나 A: "근접 경고! 컨베이어 벨트에서 물러나세요."
페르소나 B: "화학물질 유출 감지! 즉시 대피하세요."
다중 모드 경고:
시각적: 깜박이는 표시등 또는 대시보드 경고.
오디오: 인터콤을 통해 알람이 울립니다.
햅틱(Haptic): 웨어러블 기기의 진동.
피드백 루프:
작업자는 웨어러블 기기나 대시보드와 상호작용하여 상황을 확인합니다.
예: 작업자는 웨어러블 장치의 버튼을 눌러 허위 경보를 해제할 수 있습니다.
5. 지속적인 학습
페르소나 개선:
센서 및 작업자 상호 작용에서 수집된 새로운 데이터로 페르소나 모델을 업데이트합니다.
효율성과 작업자 피드백을 기반으로 경보를 조정합니다.
위험 패턴 업데이트:
사고 보고서 및 기록 데이터를 사용하여 시스템에 새로운 위험 시나리오를 추가합니다.
개발사례
사용 사례: 제조 공장
환경:
작업자는 움직이는 부품이 있는 중장비 근처에서 작업합니다.
위험에는 근접사고, 피로, 위험물질 노출 등이 포함됩니다.
구현:
페르소나 모델:
페르소나 A(기계 조작자):
일반적인 작업: 기계 조작, 특정 영역 내 걷기.
위험: 움직이는 부품에 너무 가까이 다가가는 것.
페르소나 B(품질 검사관):
일반적인 작업: 제품 품질 확인, 여러 구역 이동.
위험: 위험 구역 근처에서 장기간 움직이지 않는 상태.
센서 및 감지:
비디오 카메라는 작업자의 위치와 움직임을 모니터링합니다.
레이더는 작업자의 속도와 근접성을 추적합니다.
마이크는 조난 호출이나 경보에 대한 오디오를 캡처합니다.
위험 감지:
시나리오 1: 페르소나 A는 움직이는 로봇 팔의 1미터 이내에 5초 이상 서 있습니다.
감지: 비디오와 레이더로 근접성을 확인하여 즉각적인 경고를 발동합니다.
알람: "로봇 팔에서 물러나세요!"
시나리오 2: 페르소나 B가 화학 물질 근처의 고위험 구역에서 움직임을 멈추고 "어지러워요"라고 말합니다.
감지: 레이더로 움직임이 없음을 확인하고, 오디오로 조난 신호를 감지합니다.
경보: "현기증이 감지되었습니다! 대피하고 의료 지원을 받으세요."
대화형 알람:
근로자는 다음을 통해 맞춤형 알림을 받습니다.
근처 기계의 시각적 표시기.
웨어러블 기기의 진동.
감독자는 대시보드를 통해 알림을 받습니다.
사고 후 분석:
이벤트 데이터는 페르소나 모델을 개선하기 위해 기록됩니다.
교육 세션은 사건 통찰력으로 업데이트됩니다.
예상 결과
선제적인 위험 완화:
위험이 커지기 전에 미리 감지하여 사고를 줄여줍니다.
맞춤형 안전:
경보는 작업자별로 이루어지므로 효율성이 높아집니다.
피드백 기반 개선:
지속적인 업데이트로 감지 정확도와 경보 관련성이 향상됩니다.
페르소나 모델, 센서 융합 및 대화형 경보를 통합함으로써 이 시스템은 작업자 안전에 대한 맞춤형 동적 접근 방식을 보장하여 위험을 크게 줄이고 전반적인 작업장 안전 표준을 향상시킵니다.
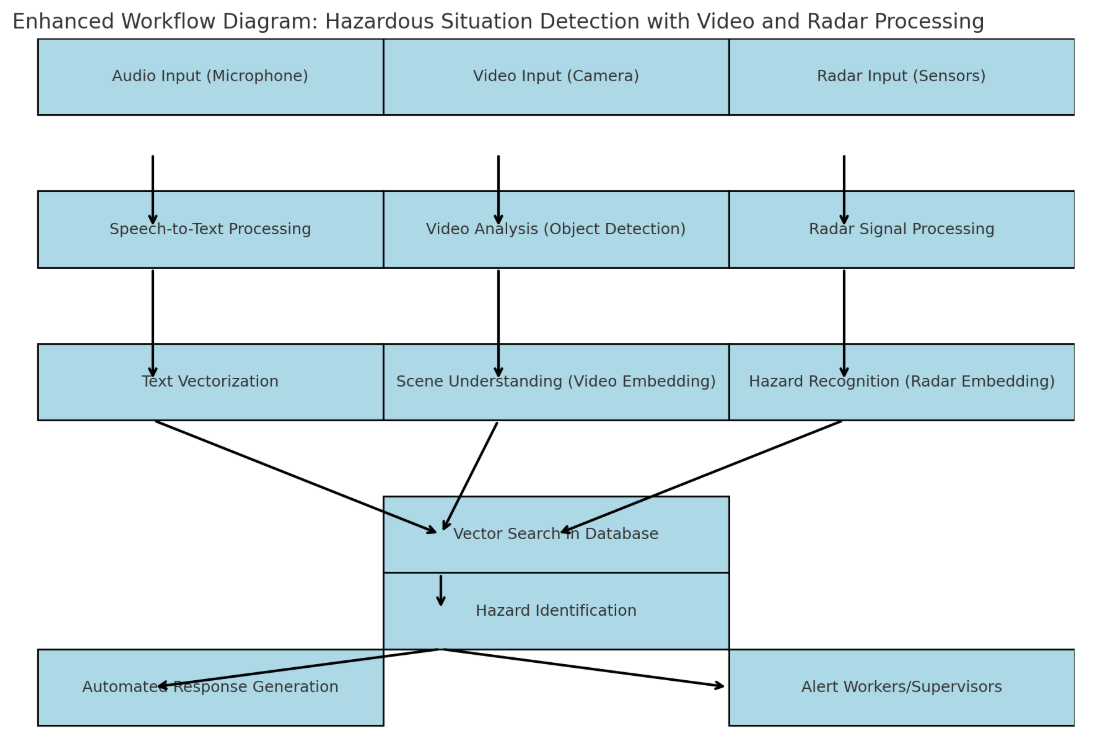
Here is the enhanced workflow diagram for hazardous situation detection. It includes additional stages for video processing (object detection and scene understanding) and radar signal processing (for spatial awareness and hazard recognition). Let me know if you need further adjustments or detailed explanations for any part of the workflow.
Development Method for Early Detection of Risk Situations and Interactive Alarm Generation Using the Persona Model Technique
Overview
To implement a system for early detection of worker risk situations and interactive alarm generation, the Persona Model Technique can be employed. This technique involves creating detailed worker profiles to personalize hazard detection and response. The system utilizes real-time data from sensors, such as audio, video, and radar, and builds on predefined worker personas to anticipate and respond to risk situations dynamically.
Key Concepts
- Persona Model:
- A persona is a detailed profile of a worker that includes their typical behaviors, movements, tasks, and environmental interactions.
- Personas are categorized based on roles (e.g., machine operator, maintenance worker), physical capabilities, and risk exposure levels.
- Interactive Alarms:
- Personalized Alerts: Based on the persona, alerts are customized in terms of urgency, delivery mode (audio, vibration, visual), and content.
- Feedback Mechanism: Workers can interact with the alarm system to confirm or resolve the issue, ensuring dynamic risk mitigation.
Development Method
1. Define Persona Models
- Data Collection:
- Gather data about workers’ typical behaviors, movements, and tasks using:
- Video monitoring for movement patterns.
- Audio analysis for voice commands or distress calls.
- Task logs for identifying repetitive actions.
- Example Persona:
- Persona A: Machine Operator
- Tasks: Operates heavy machinery.
- Risks: Proximity to moving parts, fatigue-induced errors.
- Persona B: Maintenance Worker
- Tasks: Repairs equipment, works in confined spaces.
- Risks: Falls, exposure to hazardous materials.
- Persona A: Machine Operator
- Gather data about workers’ typical behaviors, movements, and tasks using:
- Segmentation:
- Divide workers into categories such as low-risk, medium-risk, high-risk, or based on tasks and environments.
2. Hazard Detection Models
- Sensor Fusion:
- Combine data from:
- Video (detect proximity to hazardous zones or objects).
- Radar (track movement and detect falls or static positions in risk zones).
- Audio (recognize distress calls or warning sounds).
- Combine data from:
- Behavioral Analysis:
- Use persona-specific patterns to predict risk situations:
- Example: For Persona A (machine operator), if radar detects prolonged immobility near a moving conveyor belt, the system flags it as a potential hazard.
- Use persona-specific patterns to predict risk situations:
3. Early Detection Framework
- Machine Learning Models:
- Video: Object detection and pose estimation (e.g., YOLO for objects, OpenPose for human posture).
- Audio: Distress sound detection using models like Whisper or SpeechBrain.
- Radar: Movement tracking using time-of-flight signal analysis and anomaly detection.
- Event Prediction:
- Use sequence-based models like LSTMs or Transformers to detect patterns leading to hazards:
- Example: Sudden stop in worker movement + audio detection of "Help!" = Potential fall.
- Use sequence-based models like LSTMs or Transformers to detect patterns leading to hazards:
4. Interactive Alarm System
- Dynamic Alarm Generation:
- Alarms are tailored to the persona and the severity of the situation:
- Persona A: "Proximity Warning! Step back from the conveyor belt."
- Persona B: "Chemical spill detected! Evacuate immediately."
- Multi-modal alerts:
- Visual: Flashing lights or dashboard warnings.
- Audio: Alarms over the intercom.
- Haptic: Vibrations on wearable devices.
- Alarms are tailored to the persona and the severity of the situation:
- Feedback Loop:
- Workers confirm the situation by interacting with wearable devices or dashboards.
- Example: A worker can press a button on their wearable device to dismiss a false alarm.
5. Continuous Learning
- Persona Refinement:
- Update persona models with new data collected from sensors and worker interactions.
- Adapt alarms based on the effectiveness and worker feedback.
- Risk Pattern Updates:
- Add new hazard scenarios to the system using incident reports and historical data.
Development Case
Use Case: Manufacturing Plant
- Environment:
- Workers operate near heavy machinery with moving parts.
- Risks include proximity accidents, fatigue, and hazardous material exposure.
- Implementation:
- Persona Models:
- Persona A (Machine Operator):
- Typical tasks: Operating machines, walking within a specific area.
- Risks: Getting too close to moving parts.
- Persona B (Quality Inspector):
- Typical tasks: Checking product quality, moving across multiple zones.
- Risks: Prolonged immobility near hazardous zones.
- Persona A (Machine Operator):
- Sensors and Detection:
- Video cameras monitor worker positions and movements.
- Radar tracks worker speed and proximity.
- Microphones capture audio for distress calls or alarms.
- Hazard Detection:
- Scenario 1: Persona A stands within 1 meter of a moving robotic arm for >5 seconds.
- Detection: Video and radar confirm proximity, triggering an immediate warning.
- Alarm: "Step away from the robotic arm!"
- Scenario 2: Persona B stops moving in a high-risk zone near chemicals and says, "I feel dizzy."
- Detection: Radar confirms lack of movement, audio detects distress call.
- Alarm: "Dizziness detected! Evacuate and get medical help."
- Scenario 1: Persona A stands within 1 meter of a moving robotic arm for >5 seconds.
- Interactive Alarm:
- Workers receive personalized alerts via:
- Visual indicators on nearby machines.
- Vibrations on wearable devices.
- Supervisors notified via dashboards.
- Workers receive personalized alerts via:
- Post-Incident Analysis:
- Data from the event is logged to refine persona models.
- Training sessions are updated with the incident insights.
- Persona Models:
Expected Outcomes
- Proactive Risk Mitigation:
- Hazards are detected before they escalate, reducing accidents.
- Personalized Safety:
- Alarms are worker-specific, increasing effectiveness.
- Feedback-Driven Improvements:
- Continuous updates improve detection accuracy and alarm relevance.
By integrating persona models, sensor fusion, and interactive alarms, this system ensures a tailored, dynamic approach to worker safety, significantly reducing risks and improving overall workplace safety standards.
'기술자료' 카테고리의 다른 글
| FAISS 소개: 배경, 특징, 필요성 (1) | 2024.12.09 |
|---|---|
| 위험 상황 조기 감지 및 인터랙티브 알람 생성을 위한 모의 테스트 방법 및 리빙 랩 구축 방법 (0) | 2024.12.09 |
| 텍스트 데이터 벡터화 방법 및 작업자 위험 시나리오의 예제별 테스트 (1) | 2024.12.09 |
| 임베디드 마이크 시스템(USB)을 사용하여 Ubuntu에서 심층적인 소음 억제를 구현하는 개발 방법 및 예제 (1) | 2024.12.09 |
| 공장과 같은 시끄럽고 노이즈가 많은 환경에 적합한 오디오 처리 모델과 적용 방안 (2) | 2024.12.08 |

